System Architecture
Enterprise RAG platform built with Domain-Driven Design principles
Tech Stack
Backend (SoRag)
FastAPI 0.104.1 - Web framework
LangGraph 0.2.50 - Orchestration
LangSmith 0.3.45 - Observability
SQLAlchemy 2.0.23 - ORM
PostgreSQL - Primary database
FAISS 1.7.4 - Dense vectors
Elasticsearch 8.11.0 - Sparse vectors
Frontend (RagChat)
Next.js 15.3.0 - React framework
React 19.0.0 - UI library
TypeScript 5.6.3 - Type system
Vercel AI SDK 5.0.26 - AI integration
Radix UI - Accessible components
Tailwind CSS 4.1.13 - Styling
NextAuth v5
Admin (AosoRag)
ABP.io Framework - DDD framework
.NET Core - Backend
Entity Framework - ORM
OpenIddict - OAuth 2.0/OpenID Connect
Others
OpenAI GPT-4
Fine-Tuning an Embedding Encoder (MPNet) for Medical Data
Ollama (Local)
Docker Compose
Google Cloud VM
Artifact Registry
Caddy reverse proxy
High-Level Overview
Admin Client App, Frontend Client App, Backend Service:
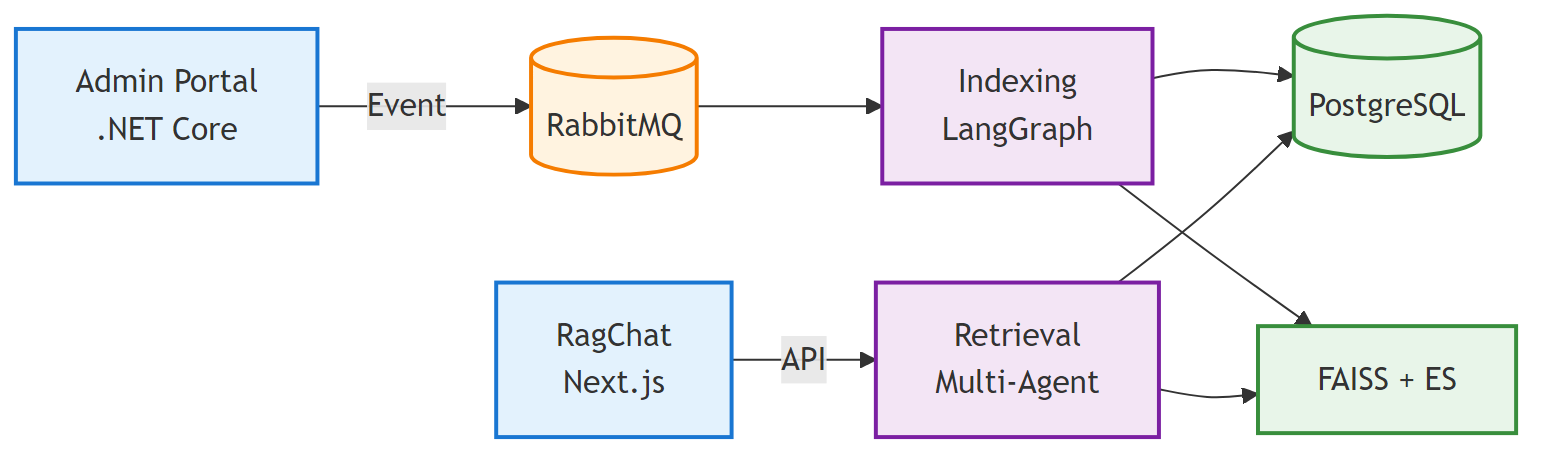
System Overview
Admin Client App, Frontend Client App, Backend Service:
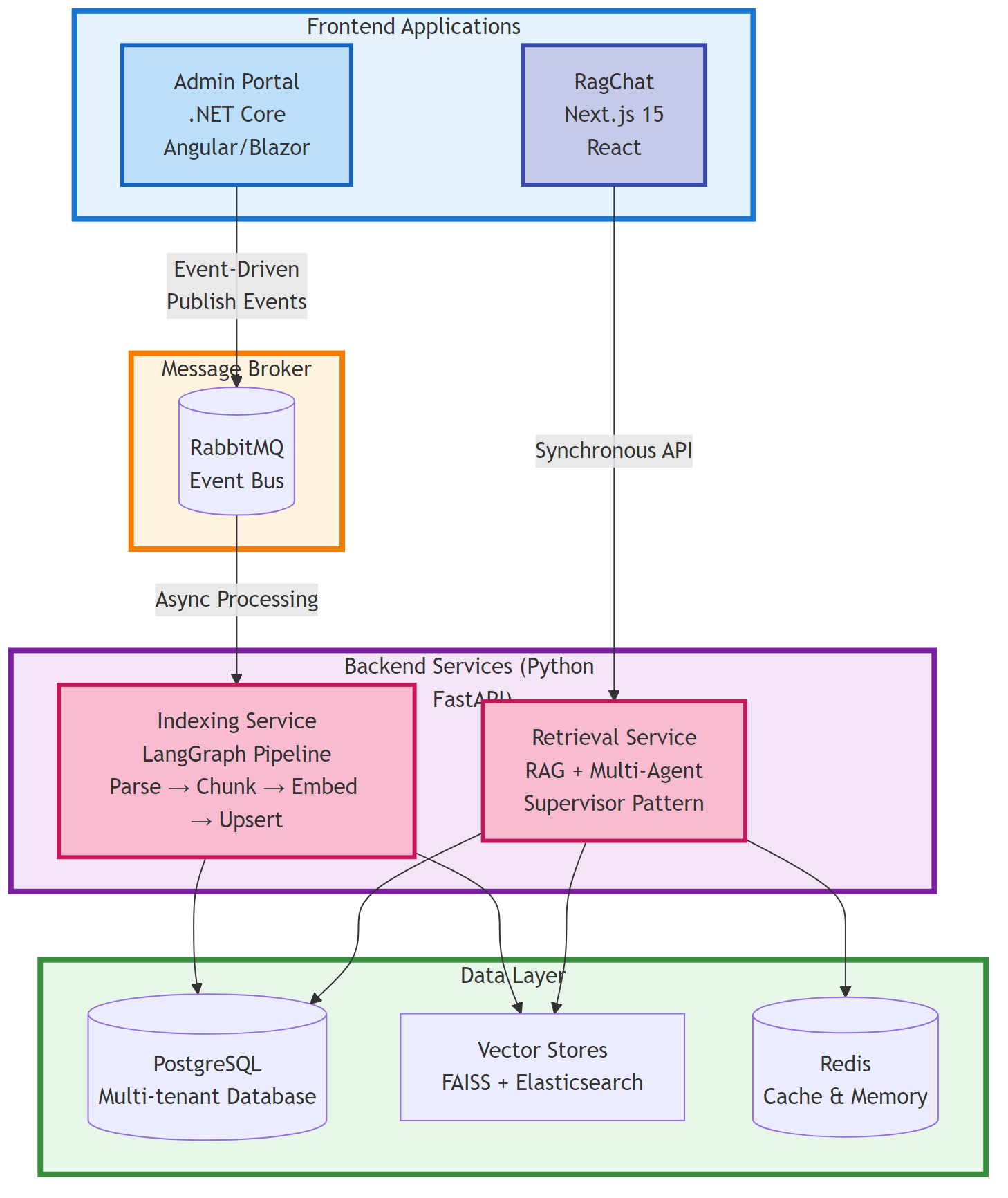
Admin and Indexing Overview
Admin Client App, Frontend Client App, Backend Service:
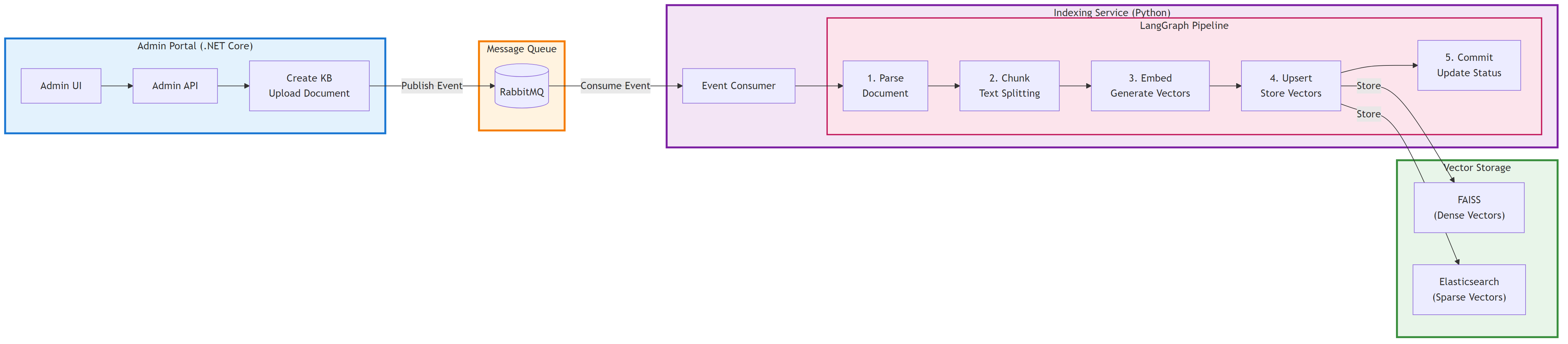
SoRag Architecture References
Below are several reference pages that illustrate the core architecture of the SoRag system, including retrieval, indexing, and historical documentation. Each link opens in a new tab.
- 🔹 SoRag Retrieval Architecture Overview of how queries are processed and retrieved within the SoRag system.
- 🔹 SoRag Indexing Architecture Explanation of document ingestion, parsing, chunking, embedding, and indexing workflows.
- 🔹 SoRag System Architecture Documentation (Old) Legacy system architecture documentation in English.
- 🔹 SoRag 系统架构文档 (Old) Legacy system architecture documentation in Chinese.
Architecture Principles
LangGraph Workflows
Observability - LangSmith full-chain tracing
Maintainability - Node-based design
Recoverability - Checkpointer support
Testability - Independent node testing
✅ Multi-Agent Architecture
Specialization - RAG/Chat/Integration separation
Parallelization - asyncio.gather concurrency
Extensibility - Registry mechanism
Isolation - Independent compilation
✅ Multi-Tenant Architecture
Automation - ContextVars + event listeners
Security - Database-level auto-filtering
Flexibility - Context Manager switching
Performance - Index optimization
✅ DDD Design Principles
Layered architecture - 4 clear layers
Repository pattern - Data access abstraction
Entity - Handles business logic
Based on ABP.io principles
Core Domain Entities
Knowledge Management
KbKnowledgeBase- Knowledge base containerKbSource- Document sourcesKbChunk- Text chunks from documents
Vector Indexing
IdxChunkEmbedding- Vector embeddingsIdxVectorCollectionItem- Vector DB itemsIdxSparseCollectionItem- Sparse vectors
Indexing Pipeline
IdxIndexingTask- Background indexing jobsIdxIndexingEvent- Event tracking
Conversational AI
RetrievalConversation- Chat sessionsRetrievalMessage- Chat messagesMemoryItem- Conversation memory
Design Patterns & Principles
Domain-Driven Design (DDD)
Entities, Aggregates, Domain Services, Repositories
CQRS Pattern
Separate read and write operations for optimal performance
Event-Driven Architecture
Distributed events using CAP pattern (Inbox/Outbox)
Repository Pattern
Abstraction layer for data access operations